TM 9-243
TYPES AND USES
Saws are tools with thin, flat steel blades that have a
row of spaced notches or "teeth" along the edge. The
blade is fastened to a handle. Saws are available in
various sizes and designs depending on their use and
the material to be cut. The most common types of saws
are handsaw, (crosscut and ripsaw), backsaw, one-man
crosscut saw, two-man crosscut saw, nested saw
(keyhole and compass) and hacksaw.
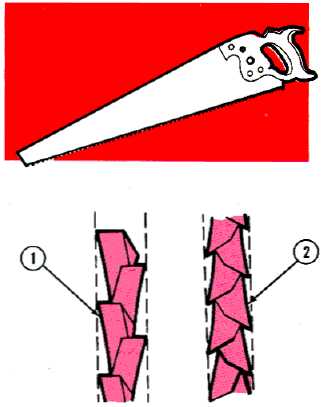
HANDSAW
The handsaw consists of a thin flat blade with teeth and
a wooden or plastic handle, called the heel, fastened to
the end of the blade by screws. There are two
categories of handsaws: the ripsaw (1) and the crosscut
(2). The ripsaw is designed to cut with the grain of
wood, and the crosscut saw is designed to cut against
the grain. The handsaw is used in carpentry, rough-out
work, and for "finish" hand sawing. Sizes of handsaws
vary depending on design and nature of the task.
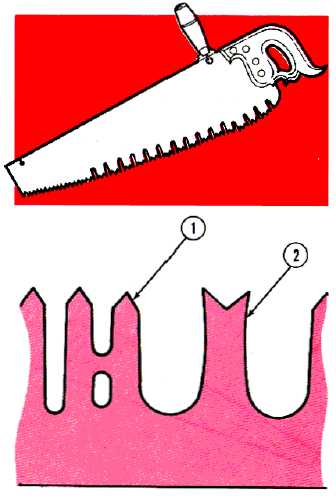
ONE-MAN CROSSCUT SAW
The one-man crosscut saw is about 36 inches long and
has a handle at one end. This type of saw is
characterized by a high-grade steel blade with two types
of teeth known as "cutters (1) and "rakers" (2). The
cutters do the cutting, and the rakers chisel out and
remove chips from the cut. It is used for heavy work
such as cutting down trees and sawing heavy timbers.
46-2